T-Mobile's $16 Million Data Breach Fine: Three Years Of Security Failures

Table of Contents
T-Mobile, a major wireless carrier, recently paid a hefty $16 million fine due to a series of significant data breaches. This penalty highlights a concerning pattern of security failures spanning three years, raising serious questions about the company's commitment to robust data protection and the effectiveness of its cybersecurity infrastructure. This article delves into the specifics of these failures, exploring the impact on consumers and the broader implications for data security in the telecommunications industry.
The 2021 Data Breach: A Massive Exposure of Customer Data
The Scale of the Breach:
The 2021 T-Mobile data breach was a massive event, affecting millions of customers. The attackers gained access to a treasure trove of sensitive information, including personal details like names, addresses, dates of birth, Social Security numbers, driver's license information, and financial data. The breach exploited vulnerabilities in T-Mobile's systems, allowing unauthorized access to its databases.
- Compromised Data: Names, addresses, dates of birth, Social Security numbers, driver's license information, financial account details, and customer account information.
- Impact on Customers: Affected customers faced a heightened risk of identity theft, fraud, and financial losses. Many spent countless hours attempting to mitigate the damage and protect their identities.
- T-Mobile's Initial Response: T-Mobile initially downplayed the severity of the breach, leading to criticism from consumers and regulatory bodies alike. Their initial communication to affected customers was also criticized for lacking clarity and sufficient support.
Regulatory Scrutiny and the Initial Fallout:
The 2021 breach triggered immediate investigations by several regulatory bodies, most notably the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). The FTC, along with state attorneys general, launched inquiries into T-Mobile's security practices and their role in the breach.
- Regulatory Bodies Involved: Federal Trade Commission (FTC), various State Attorneys General.
- Initial Statements from T-Mobile: T-Mobile issued public statements acknowledging the breach but initially minimizing its scope and impact.
- Early Public Reactions: Public reaction was swift and largely negative, with widespread criticism of T-Mobile's security practices and its communication surrounding the incident. Many consumers expressed anger and frustration over the potential risk to their personal information.
Pre-existing Vulnerabilities and a History of Security Lapses
Evidence of Prior Security Issues:
The 2021 breach wasn't an isolated incident. Evidence suggests that T-Mobile had a history of security vulnerabilities and prior breaches, indicating a systemic problem rather than a single point of failure. This pattern of repeated security failures raised serious concerns about the company's overall cybersecurity posture.
- Prior Breaches/Vulnerabilities: Reports of previous smaller-scale breaches and vulnerabilities in T-Mobile's systems existed prior to 2021, suggesting a pattern of negligence and lack of adequate preventative measures.
- Internal Audits: Findings from internal audits, if any were conducted and made public, could shed light on whether T-Mobile was aware of and adequately addressing its security weaknesses.
- Reports on Security Weaknesses: Independent security researchers and reports might highlight previously identified vulnerabilities that were not properly remediated by T-Mobile.
Lack of Proactive Security Measures:
The severity of the 2021 breach and the history of security lapses point to a lack of proactive security measures within T-Mobile. This includes insufficient investment in security infrastructure, inadequate employee training, and weak security protocols.
- Insufficient Investment in Security: Insufficient budget allocated to cybersecurity infrastructure and personnel.
- Weak Security Practices: Lack of robust authentication mechanisms like multi-factor authentication (MFA), inadequate intrusion detection systems, and insufficient security monitoring.
- Lack of Multi-Factor Authentication: The absence of widespread multi-factor authentication was a significant weakness contributing to the breach and should have been addressed long before it occurred.
The $16 Million Fine and its Implications
The FTC's Findings:
The FTC's investigation into the T-Mobile data breach revealed serious failings in the company's data security practices. The FTC cited multiple violations of data security regulations, leading to the $16 million fine.
- Key Findings from the FTC Report: The report likely detailed specific instances of negligence, inadequate security controls, and failures to comply with established data security standards.
- Specific Violations of Data Security Regulations: The FTC report likely cited violations of specific regulations related to data security and consumer protection.
- Rationale Behind the Fine Amount: The $16 million fine reflects the severity of the breach, the number of affected customers, and the magnitude of potential harm to consumers.
Long-Term Impacts on T-Mobile and the Industry:
The $16 million fine and the resulting negative publicity have significant long-term implications for T-Mobile and the broader telecommunications industry.
- Impact on Customer Trust: The breach eroded consumer trust in T-Mobile, potentially impacting customer retention and future business growth.
- Investor Confidence: The incident could negatively affect investor confidence and the company's stock valuation.
- Changes to Data Security Regulations: The incident may spur regulatory changes, stricter enforcement of existing regulations, and increased scrutiny of data security practices within the industry.
- Industry-Wide Implications: The T-Mobile data breach serves as a cautionary tale for other telecommunication companies, highlighting the need for robust cybersecurity measures and proactive risk management strategies.
Conclusion
T-Mobile's $16 million data breach fine underscores the severe consequences of inadequate data security practices. The company's repeated security failures, culminating in the massive 2021 breach, highlight the importance of robust cybersecurity measures to protect consumer data. The FTC's findings and the resulting fine serve as a stark reminder of the need for proactive security investments, strong security protocols, and rigorous employee training within the telecommunications industry.
Call to Action: Learn more about protecting yourself from data breaches and demand better data security from your wireless carrier. Research the data security measures of different providers and choose those who prioritize data security and privacy. Understanding data breach prevention strategies and advocating for robust cybersecurity practices are crucial steps in protecting your personal information. Demand better from your wireless carrier – insist on strong T-Mobile data breach prevention strategies and improved data security measures across the industry.

Featured Posts
-
 Over The Counter Birth Control A Post Roe Game Changer
Apr 22, 2025
Over The Counter Birth Control A Post Roe Game Changer
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Revolutionizing Voice Assistant Development Open Ais Latest Tools
Apr 22, 2025
Revolutionizing Voice Assistant Development Open Ais Latest Tools
Apr 22, 2025 -
 The Nationwide Anti Trump Protests A Cnn Politics Report
Apr 22, 2025
The Nationwide Anti Trump Protests A Cnn Politics Report
Apr 22, 2025 -
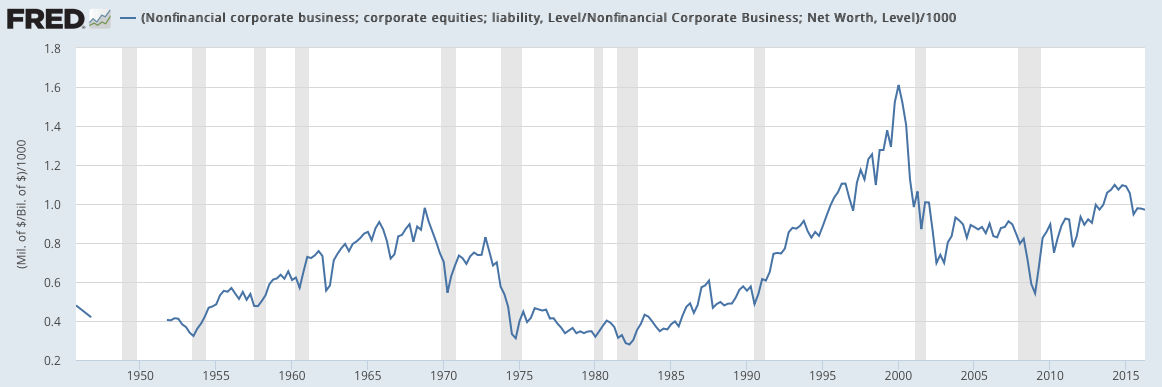 Stock Market Valuations Bof As Reassuring View For Investors
Apr 22, 2025
Stock Market Valuations Bof As Reassuring View For Investors
Apr 22, 2025 -
 2025 Razer Blade 16 Review Balancing Portability Performance And Price
Apr 22, 2025
2025 Razer Blade 16 Review Balancing Portability Performance And Price
Apr 22, 2025
