Addressing The Challenges Of Robotic Nike Sneaker Manufacturing
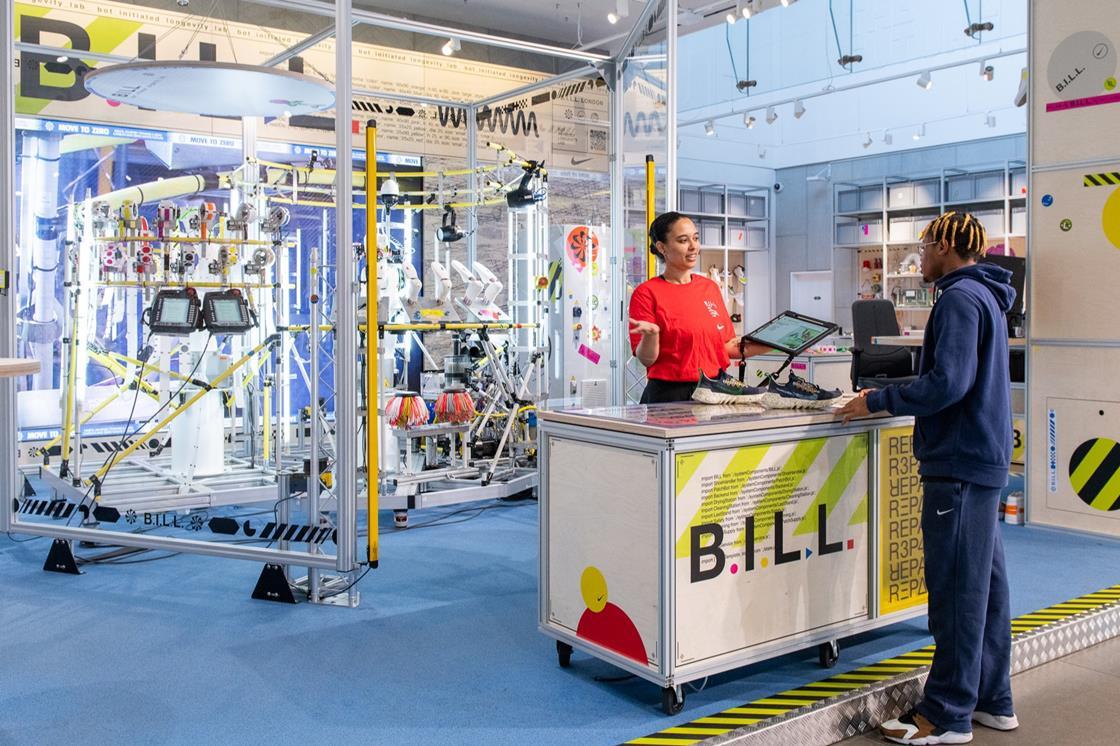

Table of Contents
Technological Hurdles in Robotic Sneaker Manufacturing
The intricate process of assembling a Nike sneaker presents a formidable challenge for robotic automation. Replicating the dexterity and precision of human hands—essential for tasks like handling delicate fabrics, applying precise glue, and executing intricate stitching—requires advanced robotic capabilities. This necessitates significant breakthroughs in several key areas: robotic precision, dexterous manipulation, and sensor technology.
Keywords: Robotic Precision, Dexterous Manipulation, Sensor Technology, AI-powered Assembly, Programmability, Defect Detection
The current limitations of robotic systems become apparent when considering the diverse materials used in sneaker construction. The flexibility of leather and the varied textures of fabrics pose unique challenges for robotic grippers and manipulators. Furthermore, the precise application of adhesive and the intricate stitching patterns demand a level of accuracy that many existing robotic systems struggle to achieve.
- Difficulty in handling flexible materials like fabrics and leather. The unpredictable nature of these materials makes consistent gripping and manipulation a significant hurdle.
- Precise gluing and stitching requirements. Achieving the necessary precision and consistency in these critical processes requires highly advanced robotic systems and sophisticated control algorithms.
- Challenges in integrating various robotic systems for a seamless workflow. Coordinating multiple robots to perform different tasks in a synchronized manner is a complex undertaking.
- Need for robust defect detection systems to maintain quality standards. Ensuring that every sneaker meets Nike's high quality standards requires advanced vision systems and AI-powered defect detection capabilities.
- High initial investment costs for advanced robotic systems. The cost of purchasing, installing, and maintaining cutting-edge robotic equipment can be substantial.
Economic and Labor Considerations in Robotic Sneaker Production
The economic implications of transitioning to robotic Nike sneaker manufacturing are substantial. While the long-term potential for reduced manufacturing costs and increased efficiency is significant, the initial investment is considerable. Furthermore, automation inevitably raises concerns about job displacement, requiring careful planning and proactive strategies to mitigate potential negative impacts on the workforce.
Keywords: Automation Costs, Job Displacement, Return on Investment (ROI), Labor Relations, Reskilling Initiatives, Manufacturing Costs
The high capital expenditure associated with purchasing and implementing advanced robotic systems represents a major barrier to entry for many manufacturers. Beyond the initial investment, ongoing maintenance, repairs, and the need for skilled technicians to program and operate these systems contribute to the overall cost. The potential for job losses in traditional manufacturing roles is another critical consideration, requiring proactive measures such as reskilling and retraining initiatives to prepare employees for new roles within the automated production environment.
- High initial investment costs for robotic systems and infrastructure. This includes the cost of robots, software, integration, and training.
- Potential job losses in traditional manufacturing roles. This necessitates careful planning and investment in reskilling programs.
- Need for skilled technicians to maintain and program robots. This requires a shift in the workforce skillset and potential investment in training.
- Economic benefits of increased efficiency and reduced production costs. These benefits will only be realized over the long term after overcoming the initial hurdles.
- Importance of strategic planning and employee training. Proactive measures are crucial for successful implementation and minimizing negative social impacts.
Overcoming the Challenges: Strategies for Successful Robotic Sneaker Manufacturing
Despite the significant hurdles, the potential benefits of robotic Nike sneaker manufacturing are too substantial to ignore. Successful implementation requires a strategic approach that embraces innovative technologies and proactive workforce management. The future lies in collaborative approaches, where humans and robots work together to optimize the production process.
Keywords: Collaborative Robots (Cobots), Human-Robot Collaboration, Adaptive Robotics, Modular Robotics, Industry 4.0, Smart Factories
One promising solution lies in the adoption of collaborative robots (cobots). Cobots are designed to work alongside human workers, enhancing productivity and precision without completely replacing human labor. Adaptive robotics, capable of adjusting to variations in materials and designs, are also crucial for flexible and efficient production. Furthermore, modular robotic systems allow for easier reconfiguration and adaptation to changing production needs.
- Implementation of collaborative robots for specific tasks. Cobots can handle repetitive or delicate tasks while humans focus on more complex operations.
- Use of adaptive robotics to handle material variations. This allows for greater flexibility and efficiency in handling diverse materials.
- Development of modular robotic systems for flexible production lines. This enhances adaptability and reduces downtime.
- Integration of AI and machine learning for improved efficiency and quality control. AI-powered systems can optimize workflows, detect defects, and improve overall performance.
- Investment in training and development programs for employees. Reskilling and upskilling initiatives are critical for a successful transition to automation.
Conclusion
The challenges of robotic Nike sneaker manufacturing are significant, encompassing technological hurdles, economic considerations, and workforce implications. However, the potential benefits—increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved consistency—are too compelling to ignore. Successful implementation hinges on a strategic approach that leverages innovative technologies such as cobots and adaptive robotics, embraces Industry 4.0 principles, and prioritizes workforce training and reskilling. The future of Nike sneaker manufacturing hinges on successfully addressing these challenges. Continue exploring the advancements in robotic technology and their impact on the footwear industry to understand the complete picture of automated shoe production.

Featured Posts
-
 Open Ai Under Ftc Scrutiny Chat Gpts Future In Question
Apr 22, 2025
Open Ai Under Ftc Scrutiny Chat Gpts Future In Question
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Open Ais 2024 Developer Event Easier Voice Assistant Creation
Apr 22, 2025
Open Ais 2024 Developer Event Easier Voice Assistant Creation
Apr 22, 2025 -
 The Robotic Hurdles In Nike Sneaker Production
Apr 22, 2025
The Robotic Hurdles In Nike Sneaker Production
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Harvard Faces 1 Billion Funding Cut Trump Administrations Anger Explodes
Apr 22, 2025
Harvard Faces 1 Billion Funding Cut Trump Administrations Anger Explodes
Apr 22, 2025 -
 5 Crucial Steps Securing A Private Credit Position
Apr 22, 2025
5 Crucial Steps Securing A Private Credit Position
Apr 22, 2025
