The Robotic Hurdles In Nike Sneaker Production

Table of Contents
Main Points:
2.1. High Initial Investment Costs and ROI Uncertainty
The Price of Automation
Implementing robotic systems in sneaker factories requires a substantial upfront investment. The cost of purchasing and installing robotic equipment, such as advanced robotic arms capable of intricate movements, automated assembly lines, and sophisticated vision systems for quality control, can run into millions of dollars. For example, a single high-precision robotic arm designed for delicate assembly tasks can cost anywhere from $50,000 to $200,000 or more, depending on its capabilities. Further costs include integration with existing systems, specialized software, and ongoing maintenance.
- Robotic Arm Costs: $50,000 - $200,000+ per unit
- Automated Assembly Line Costs: Millions of dollars depending on complexity and scale
- Software & Integration Costs: Significant ongoing expenditure
- Maintenance & Repair Costs: Unexpected expenses can significantly impact ROI.
The long-term Return on Investment (ROI) is highly dependent on several factors, including production volume, defect rates, and labor costs. A high-volume production facility might see a faster ROI than a smaller one. However, unforeseen maintenance issues and repair costs can significantly impact profitability, making accurate ROI prediction challenging.
Financial Barriers to Entry for Smaller Suppliers
The high capital expenditure required for robotic automation creates a significant barrier to entry for smaller companies within Nike's supply chain. Many smaller factories lack the financial resources to invest in such expensive technology, potentially widening the gap between large and small players in the industry. This raises concerns about the sustainability and equitable distribution of technological advancements within the broader sneaker manufacturing ecosystem. Access to financing and government subsidies could help mitigate this issue.
2.2. Complexity of Sneaker Manufacturing and Robotic Adaptation
The Nuances of Sneaker Assembly
Sneaker production is a remarkably intricate process. It involves assembling a diverse range of materials – leather, synthetic fabrics, rubber soles, laces, and various other components – with high precision and dexterity. Many tasks currently performed by human workers, such as knot-tying, stitching intricate patterns, and ensuring the precise alignment of components, require a level of manual skill and adaptability that is challenging to replicate robotically.
- Dexterity and Precision: Robots need advanced sensors and control systems for intricate tasks.
- Material Handling: Adapting robots to handle varied materials consistently is crucial.
- Human-like Skills: Replicating tasks like knot-tying and intricate stitching remains a challenge.
Programming and Software Integration Challenges
Programming robots for the nuanced tasks involved in sneaker assembly is extremely complex. It requires specialized software, skilled programmers, and extensive testing to ensure accuracy and consistency. Integrating robotic systems into existing production lines can also be challenging, potentially requiring significant modifications to the factory layout and existing machinery. Compatibility issues between different robotic systems and existing equipment can further complicate the process.
- Specialized Software: Developing and implementing suitable software is vital.
- Skilled Programmers: A shortage of skilled robotics programmers can be a bottleneck.
- System Integration: Integrating robots into existing production lines can be complex and costly.
2.3. Job Displacement and Workforce Retraining
The Human Factor in Automation
The introduction of robotics into sneaker manufacturing inevitably raises concerns about job displacement. While automation can increase efficiency and productivity, it also has the potential to displace workers performing repetitive or manual tasks. Addressing this requires a proactive and ethical approach, focusing on workforce retraining and upskilling programs to prepare employees for new roles.
- Ethical Implications: Careful planning and communication are needed to manage workforce transitions.
- Upskilling Opportunities: Retraining programs can prepare workers for roles in robotics maintenance, programming, and quality control.
- Government Support: Government initiatives can play a crucial role in supporting retraining and job placement.
2.4. Quality Control and Unexpected Errors
Maintaining Quality Standards
Maintaining consistent product quality is paramount for Nike. While robots offer the potential for increased precision and consistency, there's also the risk of defects due to robotic malfunctions or programming errors. This necessitates robust quality control systems to monitor robotic performance, identify defects, and ensure that the final product meets Nike's rigorous quality standards.
- Robotic Malfunctions: Regular maintenance and error detection systems are crucial.
- AI-Powered Inspection: Advanced AI systems can enhance quality control by identifying subtle defects.
- Human Oversight: A combination of robotic automation and human oversight is likely to be the most effective approach.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Nike Sneaker Production with Robotics
The integration of robotics into Nike's sneaker production presents a complex landscape. High initial investment costs, the intricate nature of sneaker assembly, the need for workforce retraining, and the challenges of maintaining quality control are all significant hurdles. However, the potential benefits – increased efficiency, improved quality, and enhanced production capabilities – are equally significant. Overcoming these robotic hurdles in Nike sneaker production requires a multi-faceted approach, encompassing strategic investment, technological advancements, responsible workforce planning, and robust quality control measures. We encourage further research and discussion on these challenges to unlock the full potential of automation in the footwear industry. Share your thoughts and insights on robotic hurdles in Nike sneaker production and how these challenges can be effectively addressed.

Featured Posts
-
 Gambling On Disaster The Los Angeles Wildfire Example
Apr 22, 2025
Gambling On Disaster The Los Angeles Wildfire Example
Apr 22, 2025 -
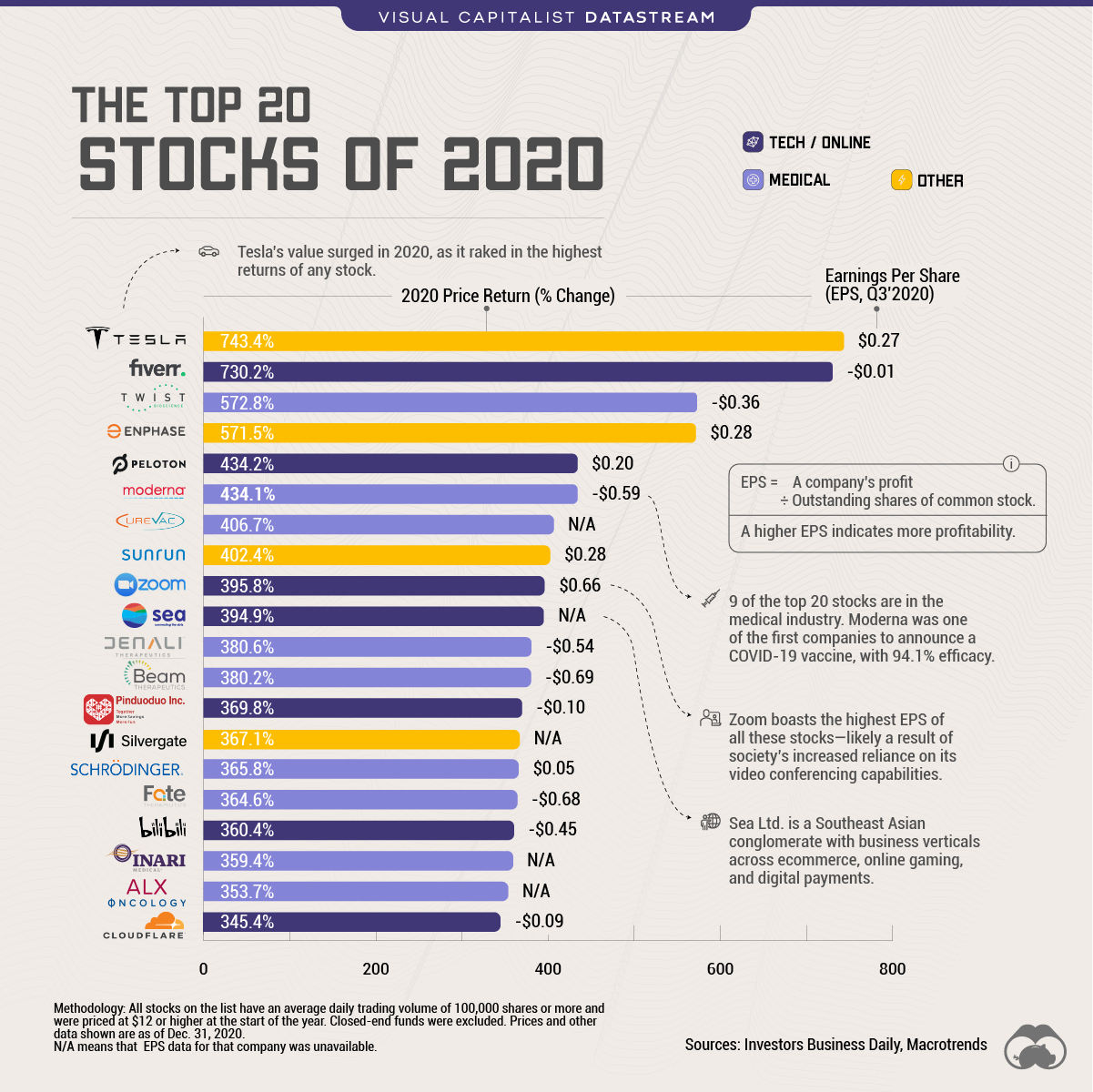 Where To Invest Mapping The Countrys Hottest Business Locations
Apr 22, 2025
Where To Invest Mapping The Countrys Hottest Business Locations
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Tracking Karen Reads Legal Battles A Year By Year Timeline
Apr 22, 2025
Tracking Karen Reads Legal Battles A Year By Year Timeline
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Hegseth Faces Backlash Over Pentagon Claims And Leaked Signal Messages
Apr 22, 2025
Hegseth Faces Backlash Over Pentagon Claims And Leaked Signal Messages
Apr 22, 2025 -
 From Scatological Data To Podcast Success Leveraging Ai For Content Creation
Apr 22, 2025
From Scatological Data To Podcast Success Leveraging Ai For Content Creation
Apr 22, 2025
